The Ultimate Guide to Studying in the UK
Tips and Advice
Exploring
10 mins read
Share

Updated at: 16 December, 2024
Published at: 12 August, 2022
By Casita Team
The Ultimate Guide to Studying in the UK
Tips and Advice
Exploring
10 mins read

Updated at: 16 December, 2024
Published at: 12 August, 2022
By Casita Team
Share
Student life is very vibrant in the UK, especially if you intend to study in London, the capital. Last year, the UK accepted 605,130 international students from all over the world. This year, the number is expected to rise to over a million. While living in the UK, you can experience a different culture, engage with natives and new communities, and study for a better future.
Higher Education in the UK
To apply to an international university in the UK, you need to be familiar with the UK's higher education system. The UK has more than 100 universities with thousands of colleges and schools to prepare students for higher education.
A university year is usually divided into two semesters, one in September and the second one in January. Most undergraduate programmes last 3 or 4 years maximum, with very few lasting 5 years. The final year of a 5-year course is usually called a “ Sandwich” year, and it is becoming highly popular with international students due to its practical nature.
Student Journey in the UK
1. Choose a Destination and a university
1. Research Destination
To choose the correct destination, check the cost of living in multiple cities in the UK. If your budget is not high, choose one of the affordable cities in the below diagram. If you have an open budget, choose a city that fits all your criteria. You can find a list of the top cities amongst international students in our blog.
2. Research and Choose Universities
If you know what you want to major in, read about the top universities in your major and how to find yours. Check the top university ranking leagues and read about the top professors in your field and where they teach. For more tips, check out our blog.
To access more info with infographics and extra details, download our expanded guide as a PDF.
3. Apply via UCAS
What is UCAS?
The UCAS, an abbreviation for Universities and Colleges Admissions Service, is a non-profit organisation that handles student admission procedures to a university. Its services include UCAS applications for undergraduates as well as application services for conservatoires and postgraduates. Use the UCAS Hub to search for the courses you like and read their requirements.
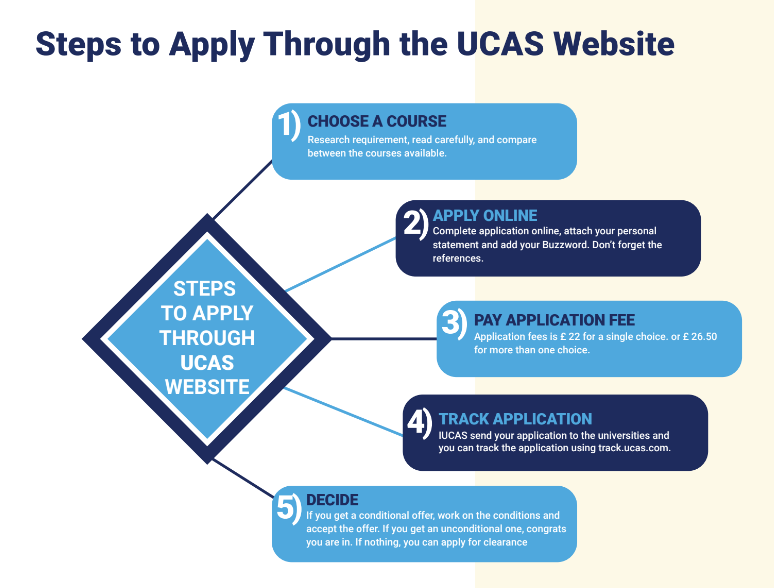
Steps to Apply Through the UCAS Website
1. Choose A Course
2. Apply online
3. Pay Application Fees
4. Track Application
5. Decide on an offer or wait for clearing to apply.
You can check the deadlines on our deadline list.
Important Details for your UCAS Application:
Your UCAS application must be accepted if you intend to apply to a university in the UK. To do so, you can use an agent to help you with the process, or you can simply apply as an independent student. If you are applying as an independent student, the following are the major documents and details you need to include in your application.
Basic Information: Your basic information, like your email, date of birth, name, parents' occupation, and financial situation, is very much needed in your application, and you can’t skip them. Make sure you write your name exactly as it is on your ID or passport. There is also an optional section for personal questions. It is up to you to answer this section. However, some universities like it when candidates are open about their backgrounds.
Education History: Ensure you add all your secondary education details, exam results and qualifications. If you haven’t graduated yet or you are still waiting for exams, sometimes UCAS can help you forward your results to universities. However, since that is not always guaranteed, it is always better to attach your results to your application. Ask your reference to add your expected results to their letter if you are still a student!
Employment History: While this section is not mandatory, it does help if you include any employment history in your application to demonstrate your commitment and responsibility. Part-time jobs count as experience for this part, so don’t hesitate to add them; however, don’t add volunteer work.
Personal statement: Your personal statement is a detrimental factor when it comes to studying in the UK. Before submitting your application, make sure you write a good personal statement and have it proofread by someone else. If you feel that you need help with your personal statement, read our tips, and you shall be fine.
Reference Letter: If you have connected your application to your school via a Buzzword, chances are your teacher has already added your reference letter to your application by the time you are done with it. If that didn’t happen though, or if you are applying independently, you can always ask a teacher or a professor to write you a reference letter and attach it to your application.
Finally, pay your application fee and submit your application to UCAS. The application will then move to universities that should either send you an offer or mark your application unsuccessful.
UCAS Terminologies You Should Know
While applying online via the UCAS system, there are several terms that you will find new to your eyes. To help you understand these terms, we have divided them into two categories: qualification terms and application terms.
Qualifications Terms:
If you are not sure what certificate you wish to pursue or you feel confused by the abbreviations you see on universities' websites, we have compiled a list of these abbreviations and their meanings to help you understand.
Abbreviation | Meaning |
DCL | Doctor of Civil Law |
DM | Doctor of Medicine |
DLitt | Doctor of Letters |
DSc | Doctor of Science |
DMus | Doctor of Music |
DPhil | Doctor of Philosophy |
DClinPsych | Doctor of Clinical Psychology |
DEng | Doctor of Engineering |
MCh | Master of Surgery |
MSc | Master of Science |
MLitt | Master of Letters |
MPhil | Master of Philosophy |
MSt | Master of Studies |
MTh | Master of Theology |
MBA | Master of Business Administration |
MFA | Master of Fine Art |
MPP | Master of Public Policy |
MA | Master of Arts |
MBioChem | Master of Biochemistry |
MChem | Master of Chemistry |
MCompSci | Master of Computer Science |
MCompPhil | Master of Computer Science and Philosophy |
MEarthSci | Master of Earth Sciences |
MEng | Master of Engineering |
MMath | Master of Mathematics or Mathematics and Statistics |
MMathCompSci | Master of Mathematics and Computer Science |
MMathPhil | Master of Mathematics and Philosophy |
MPhys | Master of Physics |
MPhysPhil | Master of Physics and Philosophy |
BD | Bachelor of Divinity |
BCL | Bachelor of Civil Law |
MJur | Magister Juris |
BM BCh | Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery |
BLitt | Bachelor of Letters |
BSc | Bachelor of Science |
Many of these degrees are also offered as either honours or non-honours degrees. You can understand the difference from our blog.
PS: For international students, some international exams and certifications could be required to prove certain essential skills for their specialisation. Check all Qualification Information Profiles on Ucas’s Website: https://qips.ucas.com/
Application Terms:
- Advisors: Advisors are mostly teachers and staff at a college, university, or school ready to help students with their applications. Sometimes you can hire an advisor from an agency to help you with your application process. If so, your advisor acts as your agent and you have to pay him for his service. However, you will have a supporter that will help you through every step, unlike volunteer advisors who provide general guidance.
- Buzzwords: A buzzword is a word you can use to link your application to your centre, school, or educational institution. This word is provided by your advisor to help them view your application and attach their references.
- Centre: Any institution that helps students with their UCAS application is considered a UCAS Centre.
- Choice: Your choice refers to the 5 courses you choose to apply for from UCAS’s list.
- Changed Course Offer: You might get an email notifying you of this offer if the university you choose changed the content of the course or changed the course altogether. A university might send you this offer if they feel a different course fits your qualifications better.
- Clearing: If you didn’t get accepted to one of your choices during the January round of UCAS, you can always apply for different courses via Clearing. Clearing shows you a list of the courses that still have vacancies and allows you to choose from them.
- Conditional Offer: This is an offer that is only applicable if you meet certain conditions. These conditions could be extra documents, exam results, or even English fluency proof.
- Confirmation: When you receive an offer, you have two options to choose from: either confirm your acceptance of the offer or decline it, in which case your insurance choice will become your main focus and you will have to wait for an offer from it as well.
- Firm Choice: Your first choice in your application.
- Insurance Choice: The second option you add to your application in case you didn’t make your first choice.
- Course: A study programme is called a course, and it could range from three years to five years in duration. These courses include undergraduate and postgraduate courses as well, including master's and PhD courses.
- Personal ID or UCAS ID: This is a ten-digit number you get from the UCAS system once you start an application. You get to use this number to complete your application if you stop midway and ask questions to customer service representatives if you face any issues with your application.
- Personal Statement: It’s an essay you have to write accurately to showcase your strengths and weaknesses. Personal statements are generally a major part of your evaluation, so make sure you prepare a good one for your application.
- Point of Entry: This point in your application refers to the year you wish to start your course. Usually, this is left blank. However, if you are transferring universities, in this case, you can add year 3 or 4 as your point of entry. Remember that you must first confirm with your university that you can begin in the 2nd or 3rd year before writing this in your application.
- Predicted Grades: If you're applying while you're still in school, your teacher will need to mention your predicted grades in the reference letter so the university will at least know what to expect from you.
- Referee: It is someone you ask to provide a reference for you. If you are applying via an advisor and you used a buzzword to link your account, your school or advisor will usually be asked to add their reference automatically via the system.
- Reference: A recommendation letter that’s written by a teacher, advisor, or professional.
- Sandwich Course: This term is used to refer to a course with an extra year of professional experience.
- Scheme Code: This is an extra code you get alongside your personal ID. Both are used to identify your application on the system.
- Tariffs: The UCAS Tariff System shifts most grades into a score that universities can use in their qualifications. While many universities don’t use that system, the ones that do are usually more flexible.
- UCAS Conservatoires: If you intend to apply for a performance-based course, you have to apply using the UCAS Conservatoires application, not the normal one.
- UCAS Postgraduate: This is the system you can use to apply for postgraduate studies.
- Unconditional offer: It’s an offer the university sends to students who fulfil all requirements. This offer means that if you want the place, you will have it instantly without any conditions. So, no extra exams or papers are required.
- Unsuccessful: If a course is marked as unsuccessful in your application, you have either not received an offer for this choice, or you didn’t meet the conditions of a conditional offer.
- Withdrawal: If you decide to withdraw from a course choice, that choice will be marked as withdrawn in your application.
Extra Terms:
Further Education College: A further education college is an institution that is not a higher education institution. It mostly offers diplomas, courses, and lessons for secondary school students or students who have left secondary school. In the USA, the term "school of continuing education" is used instead of "further education" for such establishments.
Advanced Higher: A Scottish Credit and Qualifications Framework taken by students aged 16 to 18. This is usually taken after a similar qualification award called "Higher", and it lasts a year.
CertHE: A Certificate of Higher Education that typically takes one or two years to finish.
DipHE: A Diploma in Higher Education awarded after two years.
GCSE or General Certificate of Secondary Education: It’s an academic qualification for students aged 14–16 in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
After Enrolling at a University:
Student Services Department: The Student Services Office is the office responsible for student applications, registration, examinations, and appeals.
Admissions Office: As a part of the student services department, this office is responsible for central admission systems, policies, and admission procedures.
Award Certificate: A certificate issued to students with their degree classification and date of conferral.
Date of Conferral: The date of conferral is the date of your graduation ceremony or the date your academic achievement was recognised by someone at a public ceremony.
Bank Letter: A document provided to students who wish to open a student bank account.
4. Apply for a Student Visa
Since you’re a university student, you’re eligible to apply for a student visa. This is one of the most crucial steps in your application.
UK Student Visa Requirements
- A valid passport.
- A recent photograph.
- A licensed tier-4 student sponsor.
- A bank statement (evidence of fund).
- Evidence of student accommodation.
- Confirmation of Acceptance for Studies (CAS) reference number.
- Proof of the ability to speak, read, and write in English.
When to Apply?
You should start the visa application process three months before your course starts.
Duration of Stay and Costs
Your course duration and the length of your studies will determine how long you stay. You may stay in the UK for up to five years if you are enrolled in a degree-level course. You may stay in the UK for up to two years if the course is below the level of a degree. There is an option to extend your visa if you meet the eligibility criteria. When applying for a student visa from outside the UK, it costs £348, whereas doing so from within the UK or extending an existing one costs £475. During the application procedure, there is also an additional healthcare surcharge fee that must be paid.
5. Book Accommodation
This is the final step of the process, securing a student accommodation. We know it could be much of a hassle, but Casita is here to your rescue. We offer a plethora of rooms across the UK, including ensuites, studios, and apartments. You can book the room that best suits your needs with Casita with three easy steps using Casita’s website filters.
1. Explore
This is the first stage in booking a room with Casita. Enter the city or school you plan to attend in Casita's search box. The browser will then redirect you to a new page with all the available student residences near your university or the city centre. Explore your options and use the filters to highlight preferred facilities and room types.
2. Discover
After you’ve displayed the list of properties in your chosen city, you’ll be able to see the distance between the university and these properties. Additionally, you can look up the lowest rent for each listed student accommodation.
3. Secure
This is where our dedicated multilingual accommodation experts step in. Once you've chosen the room you want, click the Enquire button. If you fill out the form's message box, our team will get your booking request and learn more about your preferences; then they’ll contact you shortly to help you secure your accommodation.
Tips and Advice
Exploring
By Casita Team
Share
Tips and Advice
Exploring
Updated at:
Published at:
By Casita Team
Share